News
DATA CENTER LIQUID COOLING PRIMARY SIDE
Data center liquid cooling primary sideIn the liquid cooling system, the primary side (Primary Loop) and the secondary side (Secondary Loop) are two independent but collaborative heat exchange cycles that together complete the heat transfer from IT equipment to the external environment. The primary side is mainly composed of a cooler, a heat exchanger, a water pump, and a primary side piping system, in which the cooler plays a core heat exchange role in the entire liquid cooling system.
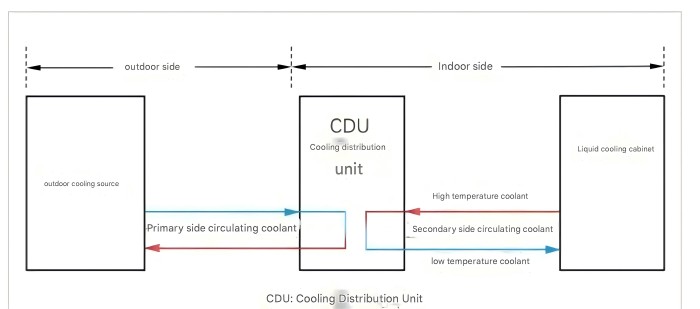
Introduction and selection of different coolers on the primary side of liquid cooling
In the liquid cooling system of the data center, the primary cooler (Primary Cooler) is the core heat exchange equipment between the liquid cooling cycle and the external environment. Its main function is to efficiently discharge the heat absorbed by the liquid cooling medium (such as deionized water, fluorinated liquid, etc.) from the IT equipment to the external environment to ensure the continuous and stable operation of the liquid cooling system. At present, the outdoor primary side coolants of data center liquid cooling mainly include cooling towers (open, closed), dry coolers, and mixed flow cooling . Different types of coolers are selected according to different regions, climates, sites, and budgets.

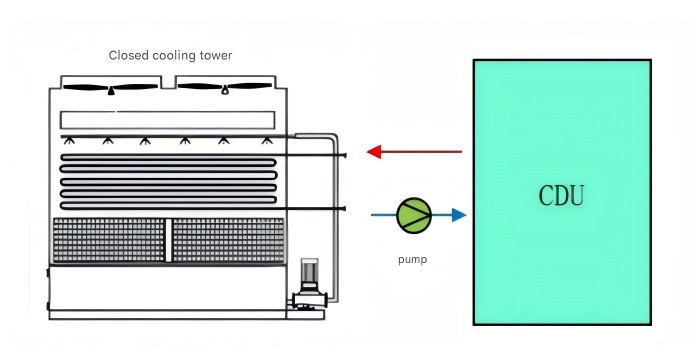
1. Closed cooling tower
The closed tower circulates the coolant (primary side) through the internal coil, and sprays the external spray water (secondary side) on the coil surface, using evaporative heat dissipation and air convection to take away the heat. The closed cooling tower consists of an internal loop and an external loop. The internal loop provides cooling water to the system. It is a closed system, so the water quality is relatively good and no additional plate exchange is required. The main advantage of the closed cooling tower is that the heat dissipation of a single unit is huge, up to 5000kw, and it occupies a small area, has low power consumption, is relatively cheap, has low maintenance costs, and has relatively stable water quality. The main disadvantage is that it consumes a lot of water.
2.Open cooling tower Open cooling tower is widely used in various cooling scenarios.
The coolant of the open cooling tower is directly exposed to the air, and forms a water film or water droplets through spraying, which evaporates and dissipates heat by direct contact with the air. The air is driven by the fan to take away heat and steam.
Its advantages are high heat dissipation efficiency, small footprint and simple structure, low initial investment and low price. The disadvantages are high WUE and poor operating water quality. Therefore, when used in a liquid cooling system, it is necessary to add a plate exchanger and a pump group at the outlet of the cooling tower to avoid scaling of the CDU plate exchanger.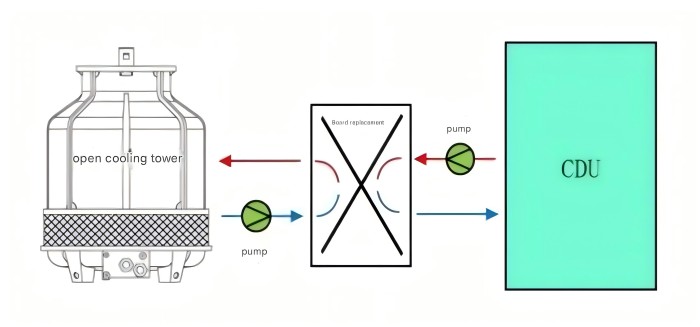
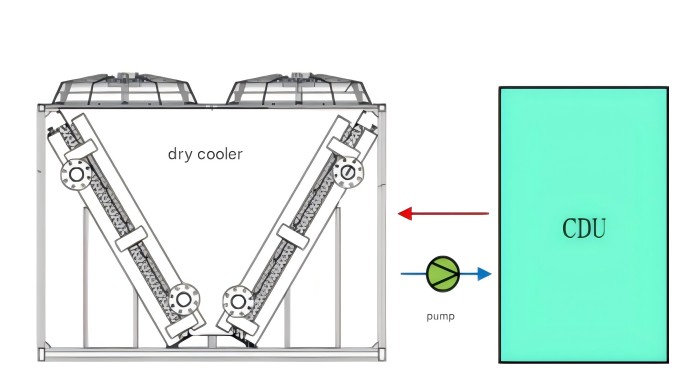
3. Dry cooler Dry cooler is a dry cooler, which completely relies on air convection to dissipate heat.
The coolant flows in the fin tube, and the fan forces the air to blow over the surface of the fin tube. The heat is directly transferred to the air without water evaporation. Its tube contains coolant, which directly exchanges heat with the ambient air, and no water is consumed during the working process. The advantages are that the WUE is 0 (or very low) and the price is cheap. The disadvantage is that the heat exchange efficiency is low and it has high requirements for air quality and ambient temperature. The dry cooler can also be equipped with a water spray system to enhance the heat exchange capacity in high temperature seasons.
4. Mixed flow cooler
Combining the two modes of dry cooling and evaporative cooling, the dry cooling mode only uses air convection to dissipate heat at low temperatures, while the wet cooling mode starts spray evaporation at high temperatures to enhance heat dissipation efficiency.
The main advantage is the balance between energy efficiency and water saving. The wet mode is activated at high temperatures to improve efficiency, and the dry mode is activated at low temperatures to save water. It has a wide range of climate adaptability and is suitable for areas with large temperature differences between day and night or seasons. The disadvantage is that the system is complex, requiring a dual heat dissipation structure and intelligent control system, which is costly and increases the difficulty of initial investment and operation and maintenance.
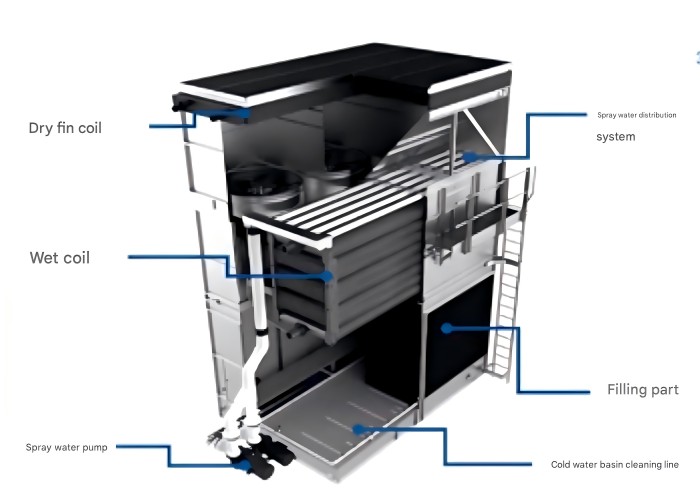
5. Adiabatic Cooler
Adiabatic products are air coolers or condensers with adiabatic precoolers. Before the fan draws ambient air into the finned coil, the air is adiabatically precooled as it passes through the humidification pad. This evaporates moisture from the air, increasing cooling capacity .
The main advantages are high efficiency and water saving, a small amount of water spraying can significantly improve the heat dissipation capacity, strong adaptability to high temperatures, and excellent performance in dry and hot climates. The main disadvantages are that water quality management is difficult, water spraying needs to be treated to prevent scaling, it is humidity sensitive, and its effect is limited in high humidity areas.

CATEGORIES
LATEST NEWS
CONTACT US
Name: Andy Zhou
Mobile:86 198 0409 1024
Tel:86 198 0409 1024
Whatsapp:8619804091024
Email:sales@datacenterstech.com
Add:Wusi Road NO 4399 Haiwan Town Fengxian,Shanghai,China
